Many are aware of the aims of the Open RAN (Radio Access Network), which is the O-RAN Alliance initiative, but only a few fully understand the many technical terms and buzzwords related to Open RAN. For example, many know the goals of Open RAN are:
- Disaggregation of RAN through standardized interfaces so that equipment vendors can interoperate.
- Supporting white box hardware to support open networking, flexible virtualization, and cost reduction.
However, many wonder what terms like O-DU, O-CU, RIC, Fronthaul, Midhaul, etc. are? And what is the role of each layer in the Radio Access Network?
Some struggle to find the correct information. Worst still, such information is not available in one place.
However, all these terms are so important to understand Open RAN.
Rest assured, we have made it simple by arranging this guide for you.
This guide is arranged as follows.
So, we go through the different layers of the 5G NR protocol stack from the perspective of Open RAN.
First, a word about Backhaul, Midhaul, and Fronthaul as these are the most common words encountered in RAN transport.
- Fronthaul is the interface between O-RU (O-RAN radio unit) and O-DU (O-RAN Digital unit). This interface in traditional networks is closed and highly vendor proprietary (for example, CPRI/eCPRI). This interface is at the top of the O-RAN initiative to disaggregate and standardize for vendor interoperability, i.e., creating an Open eCPRI standard.
- Midhaul is the interface between O-CU ( O-RAN Central unit) and O-DU ( Open RAN Digital unit). This interface is not vendor proprietary as it is defined by 3GPP. Also popularly known as the F1 interface.
- Backhaul is what we traditionally know, the interface between O-CU and the core of the network. This is traditionally an open interface. It is the interface between BBU (baseband unit) and core in traditional networks.
Now let’s turn attention to open components and interfaces defined by O-RAN Alliance.
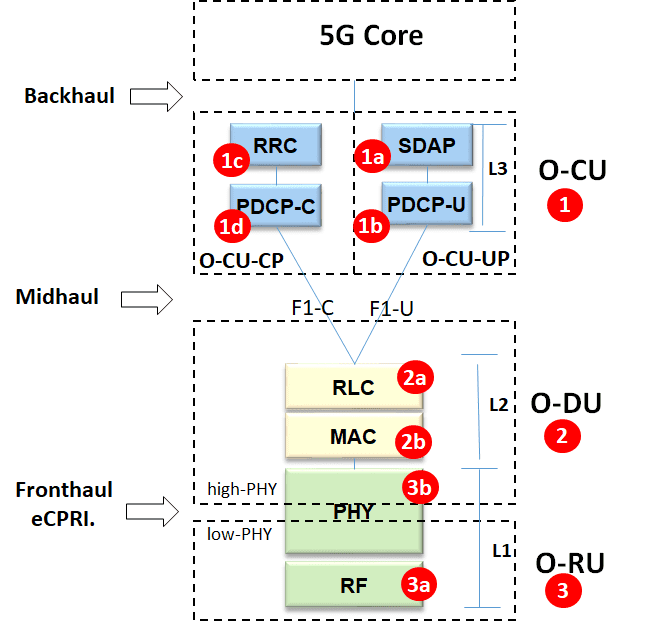
Different Protocol Layers in the 5G NR protocol stack are following.
1) O-CU (O-RAN Central Unit)
O-CU stands for Open Central Unit. Central Unit runs the layer 3 protocol in RAN and hosts RRC, SDAP, and PDCP protocols and is further divided into two subparts.
O-CU-CP ( O-RAN Central Unit-Control Plane)
This runs the control part of the CU and has two further functional blocks as follows.
1a) SDAP (Service Data Adaptation Protocol)
SDAP is a new layer introduced in 5G, present only in the user plane. It has two main roles.
- Maps between a QoS flow and data radio bearer
- Marks QoS flow ID in uplink and downlink packets
1b) PDCP-U (Packet Data Convergence Protocol-User)
PDCP allows mapping packet data units (PDUs) to multiple logical channels and sends them over different carriers. PDCP-U runs the user part of the PDCP protocol
O-CU UP (O-RAN Central Unit-User Plane)
This runs the user part of the CU. It hosts SDAP Protocol and the user plane of the PDCP protocol.
1c) RRC (Radio Resource Control)
RRC is part of the control protocol. The primary functions of the RRC protocol include connection establishment and release, broadcast of system information, radio bearer establishment, RRC connection mobility procedures, paging notification/release, and outer loop power control.
1d) PDCP-C (Packet Data Convergence Protocol-Control)
PDCP allows mapping packet data units (PDUs) to multiple logical channels and sends them over different carriers. PDCP-U runs the control part of the PDCP protocol
2) O-DU (O-RAN Distributed Unit)
O-DU is one of the most critical components in O-RAN. It is a logical node hosting RLC/MAC/High-PHY layers based on a lower layer functional split. O-DU connects with O-RU on the radio side. The interface between O-DU and O-RU is standardized by Open RAN and called open Fronthaul. This standardization will enable interworking between two vendors.
2a) RLC (Radio Link Control)
It is a layer 2 protocol; it performs the following functions
- It transfers upper layer PDUs
- It performs sequence numbering independent of the one in PDCP
- It does Error Correction through a mechanism of ARQ
2b) MAC (Media Access Control)
It is a layer 2 protocol. It performs the following functions:
- Mapping between transport channels and logical channels
- Multiplexes/demultiplexes MAC SDUs belong to one or different logical channels into/from transport blocks (TB) delivered to/from the physical layer on transport channels.
- Error correction through HARQ
2c) high-PHY Layer
It is a layer 1 protocol. PHY is the short form of Physical Layer. It interfaces the physical medium with MAC and the layers above MAC.
The PHY is split into two, low-PHY and high-PHY. The high PHY stays in the O-DUs
and low-PHY stays in the O-RUs
3) O-RU (O-RAN Radio Unit)
It is a logical node that hosts the Low-PHY layer and the RF processing board.
After discussing the NR protocol layers, let’s move to the O-RAN architecture from the management point of view.
The Open RAN has many components that need a comprehensive and robust management layer. O-RAN defines the different controllers and orchestration layers as below.
Service Management and Orchestration (SMO)
There are multiple components in SMO:
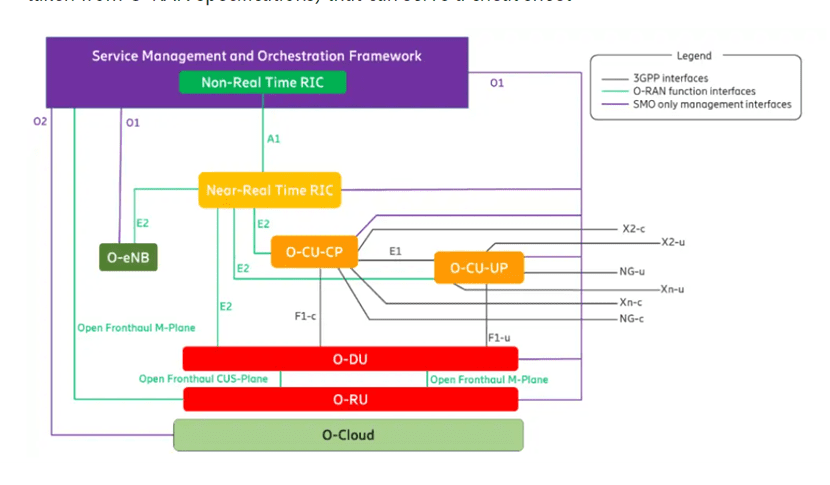
Non-RT RIC (Non-Real Time RAN Intelligent Controller)
Non-Real Time Controller (Non-RT RIC) performs FCAPs, which helps optimize. It sits at the top of the O-RAN architecture. It is called non-Real time because it processes in greater than 1 sec. It uses data analytics and AI capabilities and uses policy-based guidance
Near-RT RIC
Near-RT (Near Real Time) RIC controls and optimizes O-RAN nodes like O-CU and O-DU in near real-time. Near-RT RIC sits closer to the RAN nodes as it needs to make decisions quickly and in real-time. It uses near real-time control loops ranging from 10 ms to 1 second.
3GPP Interfaces
3GPP defined the following interfaces. O-RAN does not maintain them. T. Looking closely, the interface from the core network towards the CU are well-known interfaces towards the core. These interfaces are already interoperable between vendors. •E1 interface
- Fi-u interface
- F1-c interface
- NG-u interface
- NG-c interface
- X2-c interface
- X2-u interface
- Xn-c interface
- Xn-u interface
- Uu interface
O-RAN interfaces
O-RAN defines the following interfaces:
- A1 interface
- O1 interface
- O2 interface
- E2 interface
- Open Fronthaul interface
O-Cloud (O-RAN cloud)
As everything is virtual and Open, where do they run?
O-RAN gives the concept of Open Cloud. Which is a generic name given to the cloud infrastructure is O-Cloud. It can host different O-RAN components like O-DU, O-CU-UP, and O-CU-UP.
So that’s it about the Open RAN terminology or Open RAN glossary, which can serve as an easy reference guide!
About Lanner’s White box for Open RAN
Lanner Electronics is a leading manufacturer of white box platforms. It manufactures compact white box solutions and UCPEs for different applications like Open RAN, MEC, NFV, SDN, network orchestration, and S-WAN. It operates in the US through its subsidiary, Whitebox Solutions.
Lanner’s ECA-4025 supports the dynamic and high-performance throughputs for DU, while HTCA-E400 is a versatile platform that supports all in one carrier grade MEC applications and CU in one box.








