What is an edge server?
Edge server refers to the servers that run compute resources closer to the user, i.e., the network’s edge. Edge servers facilitate low latency services because of their proximity to the user.
Many diverse services can take advantage of this proximity, like IoT, Cloud gaming, CDN, RAN, and Mobile core service, to open the potential for new and innovative 5G use cases like uRLLC.
They are traditional servers but run at edge locations.
In contrast, the central server runs at the “Centralized Data Center.” (The traditional data center)
Edge servers are part of the Edge cloud or MEC (Multi-access Edge compute). It can be a single server or a pool of servers.
Why Edge Servers? (Benefits)
The obvious advantage of edge servers is to improve customer experience by processing functions closer to the user so that latency reduces considerably.
But that is not the only benefit. Using servers closer to the users also reduces the backhaul bandwidth, which is otherwise needed in the case of central data centers. So considerable cost savings of transport bandwidth happens.
Where is Edge Server Located?
The physical location of Edge Servers depends mainly on the type of workloads and nature of edge computing, as explained below.
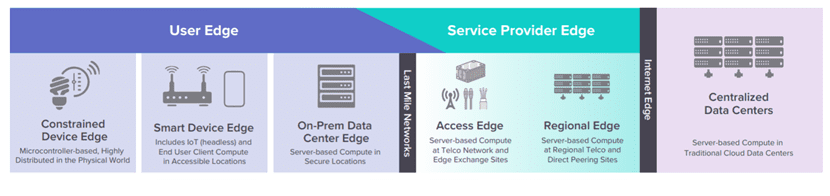
The following diagram from LFedge (Linux Foundation) summarizes the edge locations.
Two separate networks connect through the last-mile network: “User Edge” and “Service Provider Edge.”
“User Edge” spans from left to the center and includes all locations inside the customer premises. On the left boundary of the User, Edge is the “Device Edge” (edge device such as IoT device), while on the right of the User Edge is an “On-Prem Data Center Edge.”
User Edge is distinct from the Service Provider Edge as the latter is inside the service provider premises but still closer to the customer premises. The service provider owns and manages it.
Any compute servers that sit inside edge data centers are called edge servers. More specifically, they are three locations as follows:
On-Prem Edge Servers
These servers are part of the “On-Prem Edge Data Centers.” They are aggregation points inside the customer premises. One example is a private 5G network location at customer premises that can host different types of enterprise applications.
Access Edge Servers
These servers are part of the “Access Edge Data Center.” at the network edge. They are very close to the customer but within the service provider network and hence managed by the service provider. Examples include a micro data center hosted at the cellular base station or closer to the base station. Typical compute workloads include RAN services such as RU, DU, latency-sensitive gaming, autonomous vehicles, etc.
Regional Edge Servers
These Edge servers are part of the “Regional Edge Data Center.” They are aggregation points for multiple Access Edge servers. They can run services that are not as latency-critical as those running in Access Edge Datacenters.
All-in-one White Box as Edge Server
With the decentralization of the compute loads in the network, the number of edge data centers can increase quickly, increasing costs for any telco. Add to it that space and power are usually minimal on the Edge locations.
Additionally, the limited space in a micro-data center would not allow having a dedicated networking fabric of spine and leaf switches as usually present in central data centers.
Using an All-in-one smart white box solution for MEC sites can help. The economies of scale of a white box favor costs. However, such a solution should support powerful compute and robust integrated networking blades to support both compute and networking needs of edge data centers.
Lanner’s All-in-one MEC Edge Server HTCA
Lanner is a leading manufacturer of white box solutions for diverse applications such as SD-WAN, MEC, SDN, NFV, and Open RAN. Lanner operates in the US through its subsidiary, Whitebox Solutions ( whiteboxsolution.com).
Lanner’s white box platform HTCA ( HTCA-6600, HTCA-6400, HTCA-6200 ) is an all-in-one MEC/Edge data center open platform that includes a variety of compute blades and switchblades based on programmable data planes such as Intel Tofino ASIC ( such as HLM-1101). The platforms come in flexible form factors running from 2U to 6U, suitable for compact edge deployments.