How can banking/financial organizations benefit from SD-WAN?
They benefit in the same way as other industries do. For example, SD-WAN provides a way to connect new branches quickly; enables multi-WAN features with applications priority; efficient remote workers connectivity and WAN backup options, etc.
However, one another feature is more important to the financial industry-secure connectivity. Without robust security features, the WAN is deemed unusable for banks.
Therefore, in this blog, we look into how robust SD-WAN security is and how a bank can benefit from it.
But first, a couple of words on the challenges the banking industry faces today.
Challenges faced by the banking industry?
There are multiple challenges the banks are facing -On one hand, they need to worry about operational efficiencies and a better customer experience, but on the other hand, they need to protect their networks and customers from cyber-attacks.
These cyber-attacks are increasing every day. Not only that but hackers come up with new and innovative ways every day to break the security of these financial institutions. These cyber attackers want to steal personal information like social security numbers, use customers’ credit cards, and make fraudulent transfers but also attack bank networks such as DDoS, ransomware, and malware.
However, the banks, while coping with these challenges, have to stay current by constantly innovating to stay ahead of the competition.
Digital transformation is driving banks to innovate constantly.
Digital transformation is a major part of banks’ innovation. Banks need to provide new digital services as well as engage with their customers in different ways seamlessly through digital channels.
Moving the services to the cloud is a big part of this digital transformation. Cloud offers better, cheaper, and location-agnostic services. As more and more banks started using the cloud, their network planners started to re-think the WAN networking strategy.
Migration to the cloud creates new challenges.
Legacy WAN technology was good only when the services resided in the corporate DCs of the banks/financial institutions. As services moved out from the DCs to somewhere in the cloud, It creates a new challenge.
See the example below:
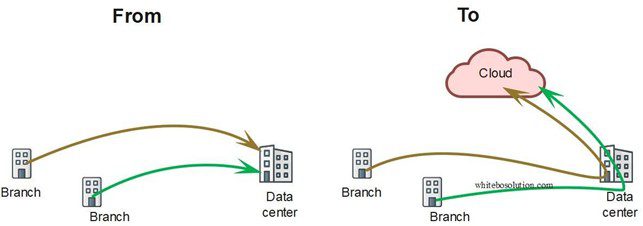 Fig: Services in DC moved to the cloud
Fig: Services in DC moved to the cloud
The latency tremendously increased as now the services need first to reach the DC, where it passes through the security screening infrastructure before getting diverted to the cloud.
Can SD-WAN be an answer to this challenge?
What is SD-WAN?
SD-WAN offers a transport agonistic and secures WAN connectivity between two endpoints by using overlay technology on top of existing underlay technologies such as the internet, MPLS, ethernet, etc. It is able to use a mix of transport underlay technologies seamlessly, resulting in better transport cost per bit, better resilience, and better application performance.
How secure can SD-WAN help the financial industry?
As SD-WAN provides secure tunnels such as IPSec and many other security features, banks can connect directly to the cloud securely without the need to route the traffic through the DC.
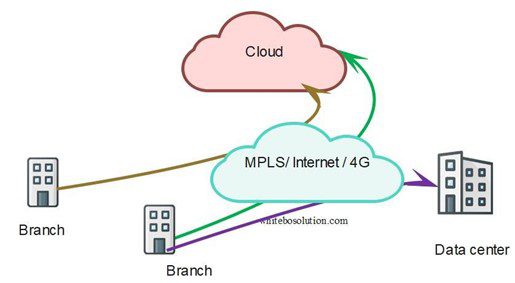 Fig: SD-WAN provides direct access to the cloud
Fig: SD-WAN provides direct access to the cloud
This solves both the security and latency issue. Not all traffic needs to transit through the DC. For example , traffic destined for trusted apps like Microsoft 365 or salesforce can be sent directly to the cloud, while some traffic still needs to be backhauled to the DC for security processing or if the applications are hosted in the DC.
Thanks to the centralized management of SD-WAN, ease of managing security policies, and many of the security features SD-WAN provides, secure SD-WAN is considered ideal for financial institutions’ connectivity.
How good is the security in the SD-WAN?
Let’s try to discuss a few of the things in the SD-WAN that make it ideal to be used in the financial industry.
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Zero trust network access means that nothing is allowed by default to enter an SD-WAN network unless it has been explicitly allowed.
Zero Trust denies implicit trust to assets or user accounts depending on their physical. Zero Trust is an answer to remote users, BYOD, and cloud assets located beyond the enterprise-controlled network boundaries. Authentication and authorization are checked before any session with an enterprise resource.
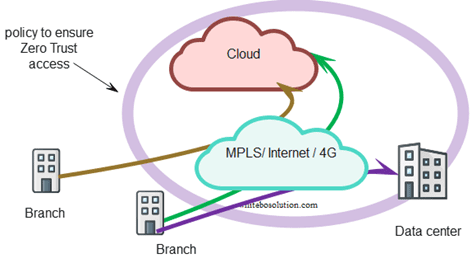 Fig: Zero Trust Network Access
Fig: Zero Trust Network Access
How is Zero trust different than VPNs?
ZTNA is different than traditional VPNs. VPN provides users with broad access to resources, potentially leading to security risks. ZTNA treats each user and device according to the permissions they have been granted and stops at the specific gateway of the application they are authorized to access.
PCI DSS Security:
The financial industry must comply with many strict regulatory requirements to protect users from potential fraud and keep financial services operations transparent. This requires secure connections between the branch locations and data centers. Also, it is required to have PCI DSS (PCI Data security standard) compliance for securing credit card holder data at point-of-sale locations and servers.
Many SD-WAN vendors now comply with these requirements making the devices suitable for use in such environments.
The following are some of the features needed to comply with such requirements.
- Stateful and next-generation firewall to provide zone-based access to different users/zones
- The credit card should not be stored on the system.
- Encryption is applied end-to-end when using public networks. These days IPSec is used by SD-WAN devices by default.
- Track and monitor all access to network resources and cardholder data. This is made possible through features such as the Role-based Active control (RBAC) feature by the SD-WAN solutions that restricts and logs every detail of the system user and the next-generation firewall.
Segmentation
Today the networks have become flat and services are reachable from anywhere. While networks have become efficient, it is also true that the attack surface has increased. Today hackers can get access to sensitive data from many points. Segmentation is the key to breaking large flat networks into subnetworks thus restricting users only to specific subnetworks they are authorized to access. Each segment is an isolated environment, and any issue in a segment is not propagated to other segments.
The traditional way to do segmentation is complex however, thanks to the centralized management and granular traffic control capabilities, segmentation is a key feature in SD-WAN.
ATM Machines’ connectivity
ATMs need secure connectivity to the data centers. The main transport used for remote machines has been VSAT. of late, cellular technologies were not considered suitable to facilitate communication between ATMs and data centers owing to the insecure nature of the transport.
Thanks to the SD-WAN’s ability to encrypt the traffic it is safe to use SD-WAN as a main or backup for the existing VSAT transport using a 4G/5G broadband connection.
How is SD-WAN Security implemented?
There are two approaches to implementing Secure SD-WAN
Security on Premises
With this approach, the SD-WAN appliance on-site is chained with the necessary security functions as VNF so that the traffic is screened locally on-site.
In the example below, the branch office traffic passes through the SD-WAN appliance but has multiple VNFs running on the same hardware, thanks to virtualization. The devices run SD-WAN, NG firewall, and IPS/IDS on the same box chained one after the other.
The traffic from the cloud passes multiple stages of security screening, like NG firewall and IPS/IDS, before it reaches the SD-WAN function itself.
Such kind of approach is called onsite or on-premises SD-WAN security.
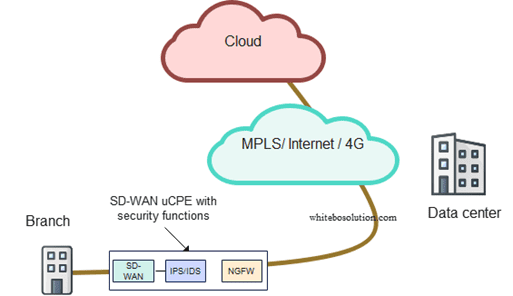 Fig: SD-WAN uCPE with on-premises security
Fig: SD-WAN uCPE with on-premises security
But it does not need to be that way.
As there is a second approach to SD-WAN security where security functions run in the cloud, also called SASE.
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
SASE is a new approach to security in SD-WAN
In the SASE approach, security is disaggregated from the SD-WAN and run in the cloud.
What is SASE?
SASE is a term coined by Gartner in 2019 that combines security in the cloud with SD-WAN on-site, so it is a combination of networking and cloud security.
Traditional SD-WAN requires security at premises as described above however, there is a reason SASE has become very popular.
As services reside in the cloud and the branch wants to reach the cloud directly, it just makes sense to run security in the cloud
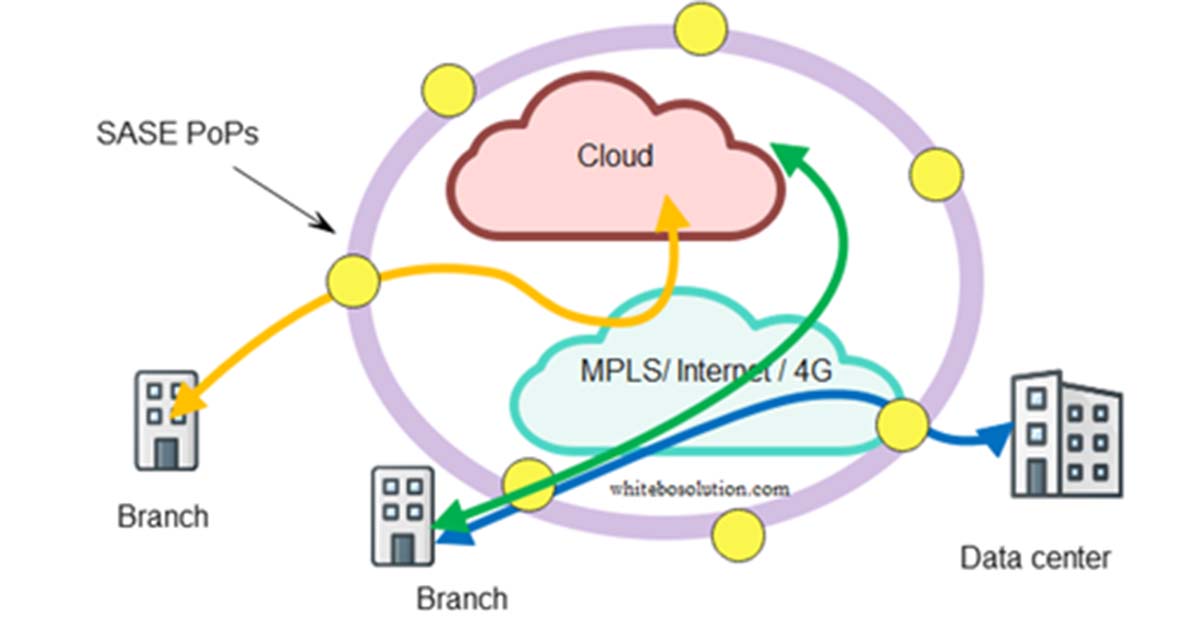
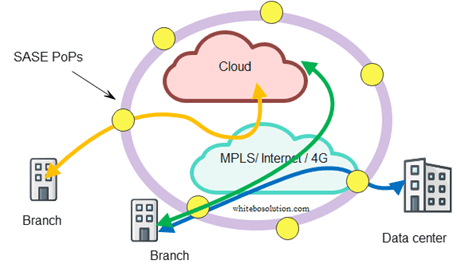 Fig: SASE cloud close to the edge
Fig: SASE cloud close to the edge
How SASE helps banking use cases?
In the SASE case, the bank branch traffic is directed to the nearest PoP where the SASE edge cloud runs. SASE runs SWG, CASB, ZTNA, and FWaaS in the cloud while SD-WAN CPE sits at the premises.
SASE advantage is branch CPE simplification, it just needs to run the networking function at the customer site from where the traffic gets backhauled to the near SASE PoP for necessary security checks.
About Lanner SD-WAN uCPEs
Lanner is a worldwide leading provider of white box solutions and universal CPEs for diverse applications like SDN/NFV, SD-WAN, Edge, Open RAN, AI, etc
Lanner offers a range of uCPEs for SD-WAN in various form factors, which can be found here
https://www.whiteboxsolution.com/whitebox-platforms/
Lanner operates in the US through its subsidiary Whitebox Solutions.